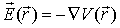The problem of generating a vector field from the
gradient of a scalar function is illustrated in electrostatics.
Here, the scalar function 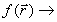 the electrostatic
potential
the electrostatic
potential 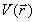 . The vector field
. The vector field 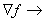 the electrostatic
field
the electrostatic
field 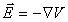 .
.
|
| (7) |
Problems of this type appear frequently in other areas of physics and engineering; for example, in heat transfer.
In Equation (7), the position vector
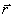 can be expressed in the
rectangular coordinates
(x, y, z),
spherical coordinates
can be expressed in the
rectangular coordinates
(x, y, z),
spherical coordinates
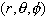 , or
cylindrical coordinates
, or
cylindrical coordinates
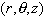 ,
the choice being made by the geometry of the problem. Similarly, the
gradient operator
,
the choice being made by the geometry of the problem. Similarly, the
gradient operator
 is to be expressed in terms of the chosen coordinates.
is to be expressed in terms of the chosen coordinates.
For a detailed discussion of the Gradient, refer to the Project Links Gradient Module
Now go on to answer some questions about what you just learned. You may also wish to examine some applications of these topics.