GEOMETRIC AND EXPONENTIAL
Analysis of the relationship between the two random variables
![[brown line]](../../../shared/graphics/pixels/brown.gif)
A geometric random variable is related to the exponential random variable. Here is the derivation:
If an interval of length T is divided into subintervals of length
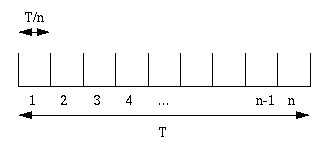
The sequence of subintervals corresponds to a sequence of Bernoulli trials with probability of success , where a is the average number of events per T seconds.
The number of subintervals until an event is a geometric random variable M.
The time until the occurance of the first event is
and the probability that this exceeds t seconds is
Applying the geometric probability pmf
As the size of the bins is decreased and thus, the number of bins is increased
If we define
which is the pdf for an exponential random variable.
This relationship is used in the relationship between Poisson & exponential random variables.
![]()
RELATED
CONCEPTSRandom Variables
Probability Density Function
Probability Mass Function
Cumulative Distribution Function
Expectation of a Discrete Random Variable
Important Discrete Random Variables
![]()
Copyright © 1998 Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. All Rights Reserved.