
Nodes can be piped into the program from file or from stdin. The syntax is as follows:
id start_point_category end_point_category
id start_point_x start_point_y end_point_x end_point_y
Points specified by category must be exactly on network nodes, while, when specifying coordinates, the next node to a given coordinate pair is used.
Attribute table will contain following attributes:
When using attributes, the length of segments is not used. To get more precise results, length should be taken indirectly into account by attributes. For example, to get the fastest path the columns 'max_speed' and 'length' are required. The correct fastest path can then be found by specifying afcol=length/max_speed (pg driver). If needed, the line length can be calculated and written to the attributes table by v.to.db.
g.copy vect=roads,myroads
v.db.addcol myroads col="forward double precision, backward double precision"
# define traveling costs as inverse of speed limit:
v.db.update myroads col=forward val=1/50
v.db.update myroads col=backward val=1/50
v.db.update myroads col=forward val=1/75 where="label='interstate'"
v.db.update myroads col=backward val=1/75 where="label='interstate'"
v.db.update myroads col=forward val=1/5 where="label='unimproved road'"
v.db.update myroads col=backward val=1/5 where="label='unimproved road'"
v.db.update myroads col=forward val=1/25 where="label='light-duty road, improved surface'"
v.db.update myroads col=backward val=1/25 where="label='light-duty road, improved surface'"
v.db.select myroads
echo "1|601653.5|4922869.2|start
2|593330.8|4924096.6|end" | v.in.ascii cat=1 x=2 y=3 out=startend col="cat integer, \
east double precision, north double precision, label varchar(43)"
v.db.select startend
#create lines map connecting points to network (on layer 2)
v.net myroads points=startend out=myroads_net op=connect thresh=200
g.region vect=myroads_net
d.mon x0
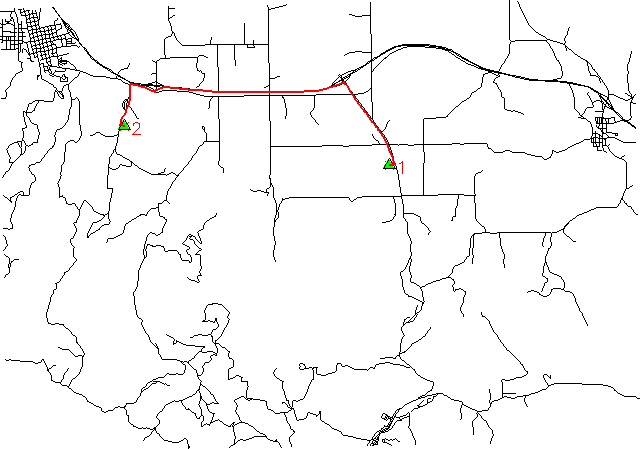
d.vect myroads_net
d.vect startend col=red
v.db.select myroads_net
d.vect myroads_net icon=basic/triangle fcol=green size=12 layer=2
d.vect myroads_net disp=cat type=point lsize=14 layer=2
# ... the 'start' and 'end' nodes have category number 1 and 2
# ID as first number, then cat1 and cat2
echo "1 1 2" | v.net.path myroads_net afcol=forward abcol=backward out=mypath
d.vect mypath col=red width=2
Last changed: $Date: 2007-08-03 05:28:13 -0700 (Fri, 03 Aug 2007) $
Main index - vector index - Full index
© 2003-2010 GRASS Development Team