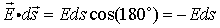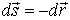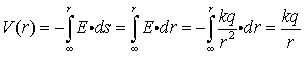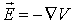Applying (4) to the case of a single charge Q, notice
|
|
|
|
|
| (5) |
Relation between V and E
Conversely, given the potential V, the electric field is obtained by
|
| (6) |
where  is the gradient operator.
is the gradient operator.
For a collection of charges, the electric field can be calculated by applying Coulomb's Law, (1), to each individual charge and adding all the contributing fields. This involves vector addition.
A much simpler method is to obtain the total electric potential by adding the potentials due to individual charge and take its gradient by (6). This is because the potential is always a scalar (a plain number), and scalars are easier to deal with than vectors.
Move on to learn the Definition of Potential. You may also wish to examine some applications of what you have just learned.