Overview
Routing in Networks: Routing Tables
A routing table has two columns:
-
The address of a destination.
-
The address of the destination of the next hop.
A Routing Table
| Destination | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | | Next Hop | * | 2 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
The above routing table at node 1 of the below network shows
the next hop for each destination.
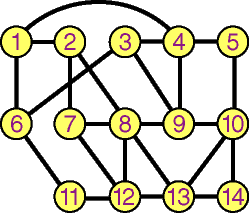 Figure 9: Figure 9: |
Every packet arriving at a router contains the address of
its destination, which can be either an endpoint or a destination
network. The router, or switch controller, consults the routing table
to decide the next hop for the packet.
| 


