Distance-Vector Routing
Ideas for Fixing the Algorithm
Path Vector:
The reason that
 propagates a distance of infinity is that when
propagates a distance of infinity is that when
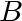 updates its path to
updates its path to
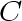 ,
it doesn't "know" that the path from ,
it doesn't "know" that the path from
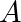 to
to
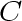 developed in the preceding stage goes through
developed in the preceding stage goes through
 . .
The path-vector idea for fixing this problem is to add
information to the distance vector to eliminate the problem just
described. One way to do this is to supply each entry in the distance
vector with a specific path which takes into account the current
estimate of the distance.
Warning: This approach may significantly increase the size
of the tables containing the distance vectors.
Split Horizon:
In the split horizon approach, a router remembers not the
whole path to the destinations, but just the first nodes of those
paths. If a neighbor of a router is the first node on such a path,
the router does not submit this information to the neighbor.
Warning: This approach eliminates the problem of counting to infinity
if the problem is caused by two adjacent routers. In more complicated
networks, the problem will persist.
Source Tracing:
The idea of source tracing is to augment the distance
vectors with the name of the router which immediately
precedes the destination on the path from the router to the
destination. If a router changes its notion of the next hop for a
destination
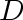 ,
then it uses the same neighbor for all destinations for which ,
then it uses the same neighbor for all destinations for which
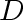 lies along the shortest path.
lies along the shortest path.
Problem
9:
Can the additional information gathered in the source
tracing method be used to reconstruct the whole path
to the destination?
Answer
Problem
10:
When and how does the information about the preceding node help to
avoid loops?
| 


